
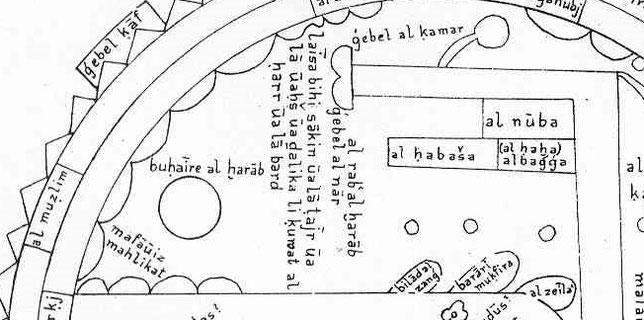
Map found in this ms
Back to Table of Contents
(5)
To next page
Ahmad ibn Al Harrani
1300 Egypt
Kitab Djamin al Founoun wa Salwat al
Mahzoun
(The Book of the Collection of Science and the Consolation of the Sadness. )
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ahmad idn Hamdan al-Harrani. The world Map is found in his Jami ’al-funun also called Gami al-funun wa-salwat al-mahzun; [The gatherer of the sciences]. It is undated, but the map closely follows the geometrical pattern of those in the Ibn al-Wardi manuscripts. The manuscript is kept: Forschungsbibliothek, MS. Orient A. 1513, fols. 46b-47a, Gotha.
Taken from: Youssouf KamaltomIVfasc1
In the land of the Zandj there are gulfs and lakes, as well as in the land of the Soudan.
The coast of al’Qoulzoum (1)…. With most of the inhabited world in the south and the west: Sana, Aden, al-Yaman, al-Chihr (2), the islands and the countries of the Soudan, the Zandj and the land
of Roum (Rome) …..
The land of Barbara. This borders the Nuba it is on the sea shore and opposite al-Yaman. The population lives in villages that border each other without open spaces. There is a mountain called
Djabal Qanoun (3): it has 7 summits, it advances into the ocean and continues under the surface of the water still for a distance of 44 miles. Up in those mountains there are small inhabited
places called al Hawiya (4) after this comes the land of the Zandj which also faces Al-Yaman and partly Sind (8). They are Soudan who are deeper black then all and they are idolaters they are all
courageous warriors…..
Their territory stretches all the way till the land of Sofala and al-Waq (9). It is a big land with many villages. Every village is situated in a bay. This land is rich in gold, in fertile lands
and in marvels, it has no cold or snow as is also the case for part of the Soudan…. There are many people in the land of the Zandj but they have little culture….. It is in this land that the Nile
splits close to the mountain al-Maqsam (10) …. From there they go to certain islands, from where they collect shells that they use as jewellery and also sell. There are big kingdoms. Among their
towns is Nikand, a very big town… and Ilyanis (12) on the shores of the Zandj sea….. This last town is situated at the end of the Zandj country and its people are idolaters…. Malanda is a town at
the sea shore in a golf with sweet water, close by is an iron mine… Then there is Manbasa a small town at the sea shore where there are also iron mines…..
The land of the Damadim (5): This land is on the Nile above the land of the Zandj. There are many people and the Soudan raid them often. They don’t care about religion. In their country
there are many giraffes. It is here that the Nile takes his direction for Misr (11) and for Zandj….
The land of Soufala the golden. This borders the Zandj on the coast. It is vast with mountains with iron mines. These mines are just by the people of the country and the people from Hind come to
buy the iron at a good price…..One of the marvels of the land of Soufala is the pure gold which is so plenty full that a grain of it might be 2 or 3 mithqals (6) heavy and more…. The land of
Soufala touches the land of al Waq-Waq (9)…..
The island of al-Qoumr (7) is large and long in easterly direction it is four months. There is a town called Sikan where resides the king. It is a very fertile island where there are trees and
fruits, coconuts, sugar cane, and rice.
Section on the sea of Zandj and its sea and marvels: This sea is in reality the same as the sea al Hind. The lands of the Zandj are situated on the southern side of the constellation Souhail. The
navigators on this sea see the south pole and not the north pole…. That river (the Nile) comes out of the Djabal al-Qamar from behind the equator. This mountain is called Mountain of the Moon,
because the moon never comes up above this mountain because it is behind the equator. The origin of the river is in the black sea of the dead that runs below the Djabal al Qamar.
(1) al’Qoulzoum; al-Qulzum: located at the head of the Gulf of Suez.
(2) al-Chihr; or Shihr; coastal town in Hadhramaut in eastern Yemen
(3) Djabal Qanoun: it has 7 summits; Khakoui, (Ras Hafun) who has seven peaks: the seven peaks on the mountain on the peninsula of Hafun still have different names (Charles Guillain p203)
(4) Hawiya: In south Somalia mentioned by Ibn Said (1250); Ahmad ibn Al Harrani (1300); Al Idris Ouns al Moubhadj (1192); Idrisi (1150) has El Hadye; Abulfida (1331); Haouiya; Dimashqi (1325) Hawiah; Al Wardi (1456) Haouina
The reference in Al-Idrisi (1150) to the Hadiye and in Ibn Sa’id (1250) to the Hawiye, on both occasions associated with the Benadir port of Merca, where the Hawiya live today, suggests that they have been in this area for at least 700 years. The references slightly later in the Futuh al-Habasha to Somali groups in north-western Somaliland indicates that the population in this area has also remained substantially unchanged since the sixteenth century, when the work was written. The Galla another group from the Horn has been living there at least since the 15th century as Fra Mauro (1459) mentions a Galla River in Ethiopia.
(5) Dendemes, Dendemeh; Dandama: East African people living in the interior, close to the sources of the Nile; also mentioned by Al Masudi (916); Al Idrisi (1150); Ibn Said (1250); Ibn al Jawzi (1257); Harrani (1300); Qadi Ibn Sasri Al-Shafi’I (1300); Al-Dimashqi (1325); Abulfida (1331); Nuwayri (1333); Cowar el-aqalim (1347); Said Abd al Aziz al Dairini (d1385); Ibn Khaldun (1406); Al Qalqashandi (d1418) and Ibn al Wardi (1456) speaks about Demadam; al Himyari (1461).
(6) mithqals: 4-5 gr of gold
(7) island of al-Qoumr: Madagascar
(8) now in Pakistan.
(9) in the books three different places are called Waqwaq: in South-East Africa; in Indonesia; around Japan. Here East Africa south of Sofala is meant.
(10) Jabal Makhasam: The mountain Muqasam El-Moquecem; Muqassim: literally symmetrically divided, close to the source of the Nile; also found in Ibn Al Wardi (1348); Hafiz I Abru (1420); Ibn Said al Maghribi (1250); Al Idris ; Ouns al Moubhadj (1192), al Harrani (1300); Abu al-Fida (1331).
(11) Misr= Egypt
(12) Al-Banas of Idrissi (1150)