


This map shows part of the hinterland of the towns Ungwana, Shaka, Mwana. In later centuries (Portuguese times) towns resembling Swahili towns came into existence in this hinterland. They so extended the hinterland even further.
Hudani or Hawadani (Ungwana)
--------------------------------------
Close to modern day Kipini village at the mouth of the Ozi river.
Ibn Majid (1470) is the only author to mention it as Hudani and also as Hawadani. There is an unsure mention on the Chinese Maokun map as Menfeichi.
Taken from: Coast-interior settlement and social relations in the Kenya coastal hinterland. By GHO Abubgu and HW Mutoro.
Swahili Monumental Architecture and Archaeology North of the Tana River by Thomas H. Wilson 2016
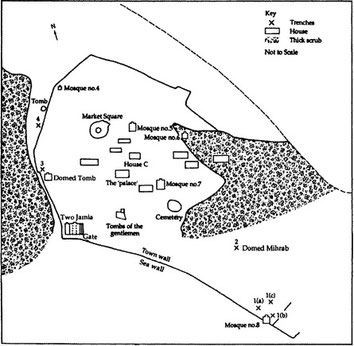
The ocean comes very close to the western edge of the town. The ruins of Ungwana extending roughly over 45 acres, were first excavated by Kirkman in the 1950s and more extensively, in 1990, by Abungu.
The town was encircled by a town wall which enclosed ruins of eight mosques, numerous houses and several groups of large monumental tombs. Northeast of the town, and adjacent to the town wall, is located a large earthen mound reputed to be the burial place of Fumo Liongo, the Swahili poet-king who is also claimed by the Pokomo people of the Tana basin to be one of them.
The excavations by Kirkman took place at the main mosque the old Jamia(14th-15th century) and the new Jamia (end 15th) (referred to as the Two Jamia -they were build wall to wall), the mosque of the Domed Mihrab, the sea wall and at the gate adjacent to the Two Jamia. Wilson (1978) also opened a sondage near the Domed Tomb, situated close to the mosque of the Domed Mihrab.
For the tombs close to the Two Jamia a date is suggested in the middle of the fourteenth century for the earliest tombs, and late fifteenth century for the later ones.
The divisions of the town are as follows: the palace (central), the central section, the south section, the commercial section, the midwest section, the western, the northern west section, the south-western section, the wells, the town wall, the mosques 1 to 7 and the burial tombs.
The town’s life is divided into six periods, with the beginnings of the settlement dated to the mid-tenth century (Abungu in 1986/7) it lasted until the seventeenth century (Kirkman 1966), when it was deserted.
The area around the settlement, like most of the coastal strip, has fertile soils and enough rainfall for farming to be carried out all year round. The availability of good soils and adequate rainfall could have been one of the factors that influenced the location of the site, for it would have yielded a dependable surplus of food and, in case of scarcity, could have been a reserve for other Tana delta settlements.
Ungwana was well placed to tap the produce of the interior, especially along the lower and mid Tana, with the river serving as a waterway; it was probably a gateway community. Wherever trade is important to the growth of a region, the most influential communities will tend to develop and be situated at strategic locales for controlling the flow of merchandise. These communities flourish at the passage points into and out of distinct natural or cultural regions, and serve as ‘gateways’ which link their regions to external trade. Ungwana, located at the mouth of the Tana (a river that traverses the forested and sometimes arid region of the interior), would have been well suited as a gateway to interior commodities on the one hand and overseas trade on the other.
The wells in the town, which can also be paralleled with others along the Swahili coast, are also similar to some of the inland types and as such are important in the study of the interaction between the coast and the interior, and of the part played by inland groups in the development of the towns. They suggest some architectural influence from the hinterland from areas such as Elwak and Wajir in North-eastern Kenya.
At its peak Ungwana was very prosperous. It was a complex society, with a high occurrence of prestige goods. In the fourteenth to seventeenth centuries AD, the town centred on groups of stone houses with a mosque nearby. At the centre of the town was a large building which appears to have belonged to a wealthy person or ruler of some sort. The structure has been referred to as the ‘palace’.
It ceased to exist as a community in the last quarter of the 17th century due to the advancement of the Galla, an Eastern Cushitic-speaking people from south-western Somalia.